Reference+
Name
bezierTangent()
Description
Calculates the tangent of a point on a Bézier curve. There is a good definition of tangent on Wikipedia.
Examples
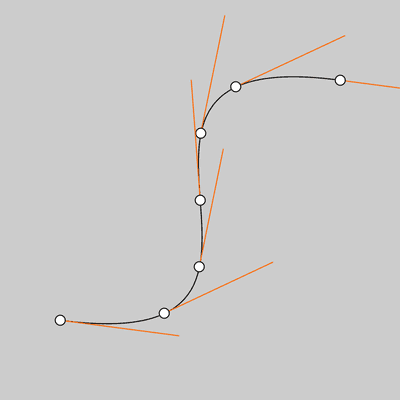
size(400,400); noFill(); bezier(340, 80, 40, 40, 360, 360, 60, 320); int steps = 6; fill(255); for (int i = 0; i <= steps; i++) { float t = i / float(steps); // Get the location of the point float x = bezierPoint(340, 40, 360, 60, t); float y = bezierPoint(80, 40, 360, 320, t); // Get the tangent points float tx = bezierTangent(340, 40, 360, 60, t); float ty = bezierTangent(80, 40, 360, 320, t); // Calculate an angle from the tangent points float a = atan2(ty, tx); a += PI; stroke(255, 102, 0); line(x, y, cos(a)*120 + x, sin(a)*120 + y); // The following line of code makes a line // inverse of the above line //line(x, y, cos(a)*-30 + x, sin(a)*-30 + y); stroke(0); ellipse(x, y, 10, 10); }![Image output for example 1]()
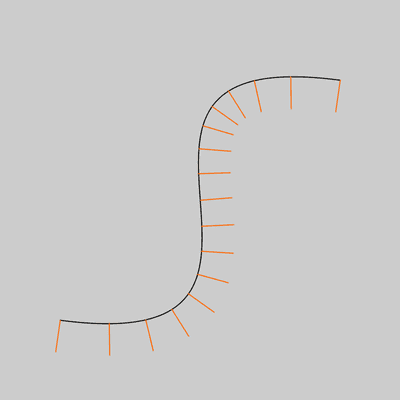
size(400,400); noFill(); bezier(340, 80, 40, 40, 360, 360, 60, 320); stroke(255, 102, 0); int steps = 16; for (int i = 0; i <= steps; i++) { float t = i / float(steps); float x = bezierPoint(340, 40, 360, 60, t); float y = bezierPoint(80, 40, 360, 320, t); float tx = bezierTangent(340, 40, 360, 60, t); float ty = bezierTangent(80, 40, 360, 320, t); float a = atan2(ty, tx); a -= HALF_PI; line(x, y, cos(a)*32 + x, sin(a)*32 + y); }![Image output for example 2]()
Syntax
bezierTangent(a, b, c, d, t)
Parameters
a(float)coordinate of first point on the curveb(float)coordinate of first control pointc(float)coordinate of second control pointd(float)coordinate of second point on the curvet(float)value between 0 and 1
Return
float

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.