Examples+
Follow 2
by based on code from Keith Peters
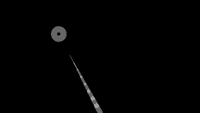
A two-segmented arm follows the cursor position. The relative angle between the segments is calculated with atan2() and the position calculated with sin() and cos().
Highlighted Features
/**
* Follow 2
* based on code from Keith Peters.
*
* A two-segmented arm follows the cursor position. The relative
* angle between the segments is calculated with atan2() and the
* position calculated with sin() and cos().
*/
float[] x = new float[2];
float[] y = new float[2];
float segLength = 50;
void setup() {
size(640, 360);
strokeWeight(20.0);
stroke(255, 100);
}
void draw() {
background(0);
dragSegment(0, mouseX, mouseY);
dragSegment(1, x[0], y[0]);
}
void dragSegment(int i, float xin, float yin) {
float dx = xin - x[i];
float dy = yin - y[i];
float angle = atan2(dy, dx);
x[i] = xin - cos(angle) * segLength;
y[i] = yin - sin(angle) * segLength;
segment(x[i], y[i], angle);
}
void segment(float x, float y, float a) {
pushMatrix();
translate(x, y);
rotate(a);
line(0, 0, segLength, 0);
popMatrix();
}
This example is for Processing 4+. If you have a previous version, use the examples included with your software. If you see any errors or have suggestions, please let us know.